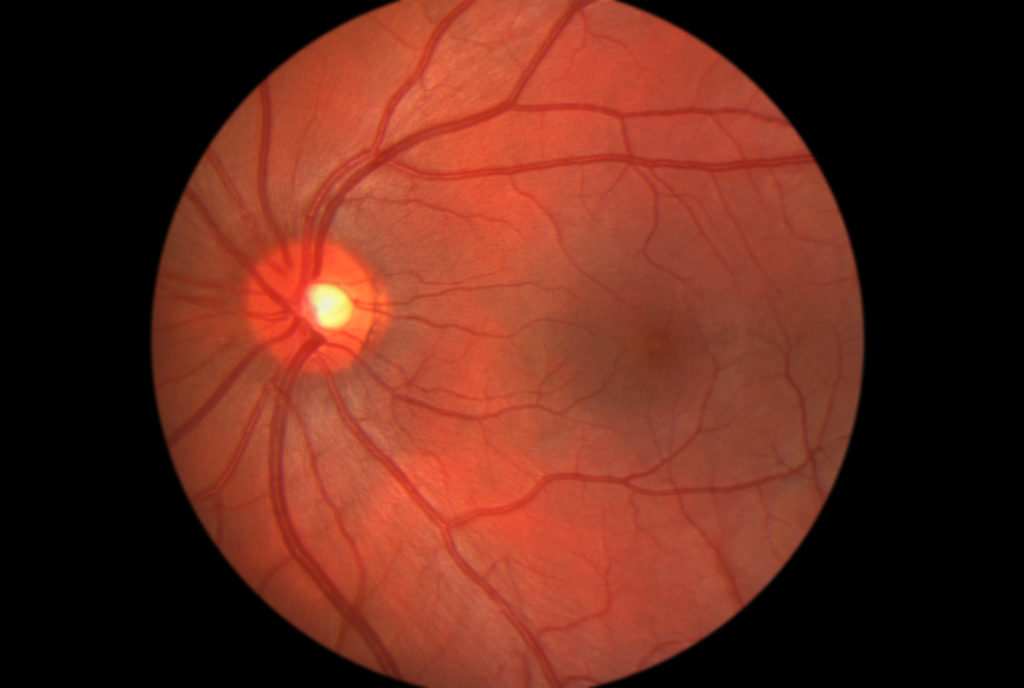
A retinal detachment can cause blindness. The most common type of retinal detachment is called a “rhegmatogenous retinal detachment” and, by definition, is cause by a retinal tear or hole in the retina.
There are other types of retinal detachment, but they are usually related to underlying disease such as diabetic retinopathy.
Symptoms of Retinal Detachment
The most common symptoms of a retinal detachment are flashes and floaters. We generally recommend that anyone who experiences new floaters or significant flashes get a dilated eye exam looking for a retinal tear or detachment.
Loss of vision from a retinal detachment starts with the peripheral vision. As the area of detachment enlarges, vision loss will gradually move to involve your central vision.
Causes of Retinal Detachment
While trauma can cause a retinal detachment, most occur retinal tears/retinal detachments are not associated with trauma.
A posterior vitreous detachment (PVD) commonly causes are retinal tear which can lead to a detachment.
Other causes include lattice degeneration, retinal holes, recent intraocular surgery or retinal tears.
Treatment for Retinal Detachment
The natural course of a retinal detachment is blindness, that is, if treatment is neglected, a retinal detachment can cause blindness.
Surgery for rhegmatogenous detachments include: scleral buckle, pneumatic retinopexy or vitrectomy. Both vitrectomy and a scleral buckle can be combined.
Technically speaking, laser is not an option for retinal detachments but is the gold standard for a retinal tear not associated with a retinal detachment.
Prognosis
The key to an excellent outcome depends upon whether or not your central vision was involved. If surgery is performed while maintaining central vision, chance are that there will be no vision loss.
Other factors affecting your visual outcome include your age, duration of the detachment and number of previous surgical attempts to repair the eye.
Recommendations
If you develop sudden flashes, floaters or are experiencing loss of peripheral vision, consult your eye doctor.